The oil and gas industry, due to its sensitive and complex nature, relies heavily on advanced instrumentation to monitor, control, and optimize processes. These tools aim to improve efficiency, minimize risks, and ensure operational safety. This article reviews the most commonly used instrumentation equipment in this industry.
1. Pressure Transmitters
Pressure transmitters are vital instruments used for measuring the pressure of fluids (liquids, gases, or steam).
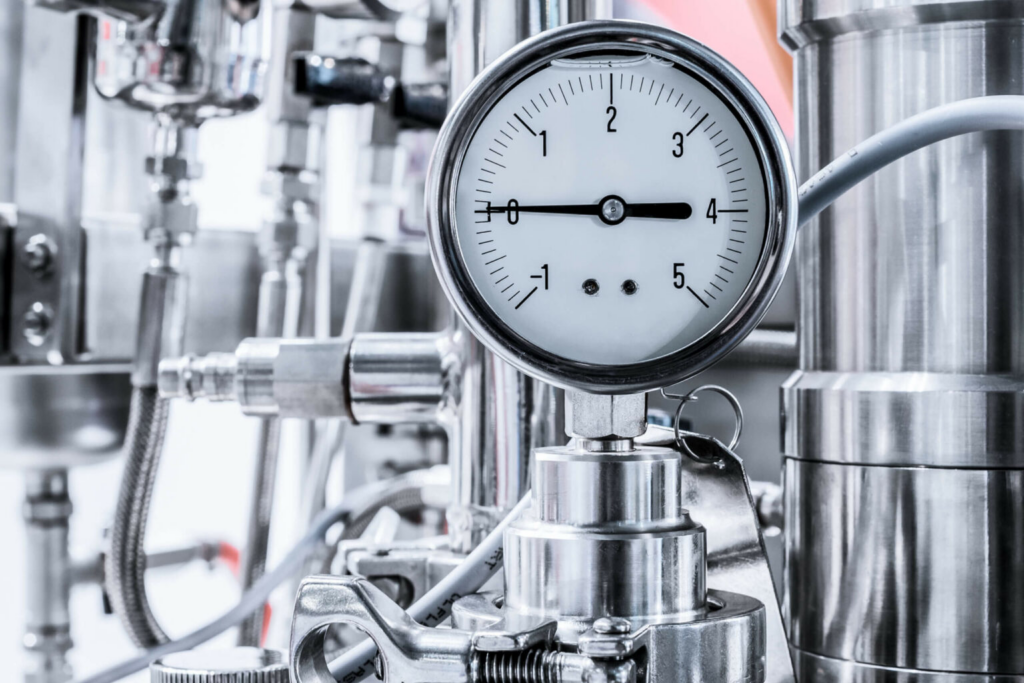

Applications:
Monitoring pressure in oil and gas pipelines.
Controlling pressure in pressurized tanks.
Preventing overpressure incidents that could lead to accidents.
Features:
High accuracy.
Resistance to harsh environmental conditions like extreme temperatures and corrosive substances.
2. Temperature Transmitters
These instruments measure temperature at various points in the process and send the data to control systems.
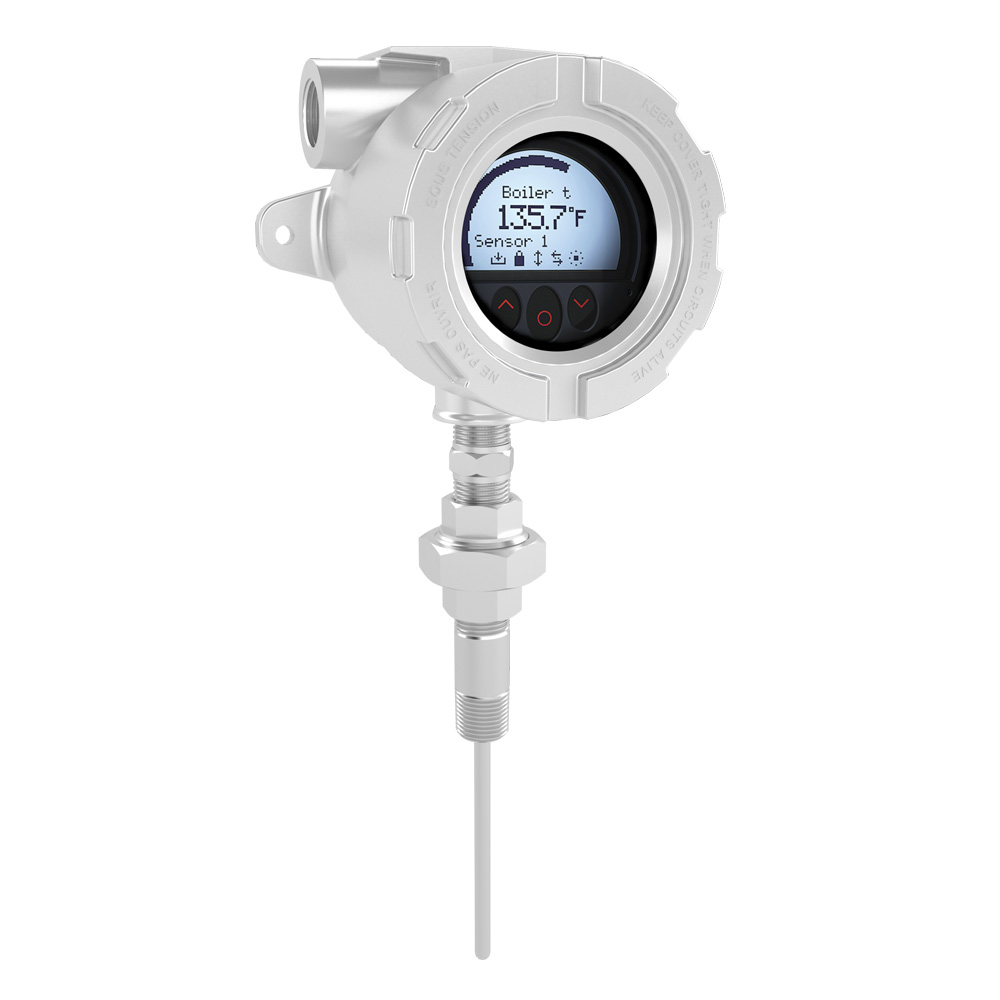

Applications:
Monitoring heat exchangers.
Controlling temperature in refining and distillation processes.
Ensuring optimal performance of heating and cooling equipment.
Features:
Ability to operate in extremely high or low temperatures.
Use of technologies such as thermocouples and RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors).
3. Flow Meters
Flow meters measure the flow rate of fluids.
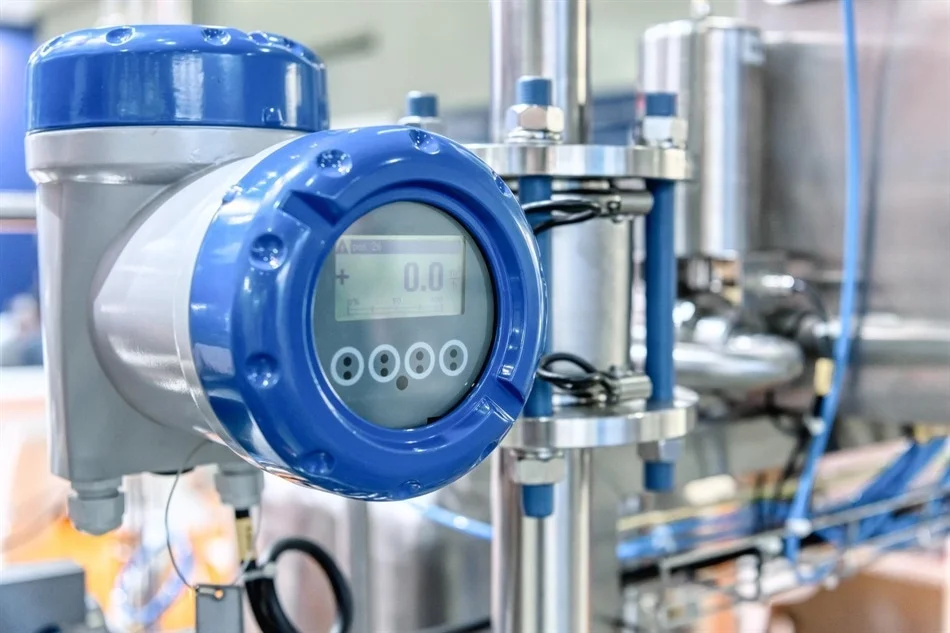

Applications:
Measuring the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
Controlling the injection rate of chemicals into pipelines.
Managing water injection in oil extraction processes.
Common Types:
Turbine flow meters.
Magnetic flow meters.
Ultrasonic flow meters.
4. Level Transmitters
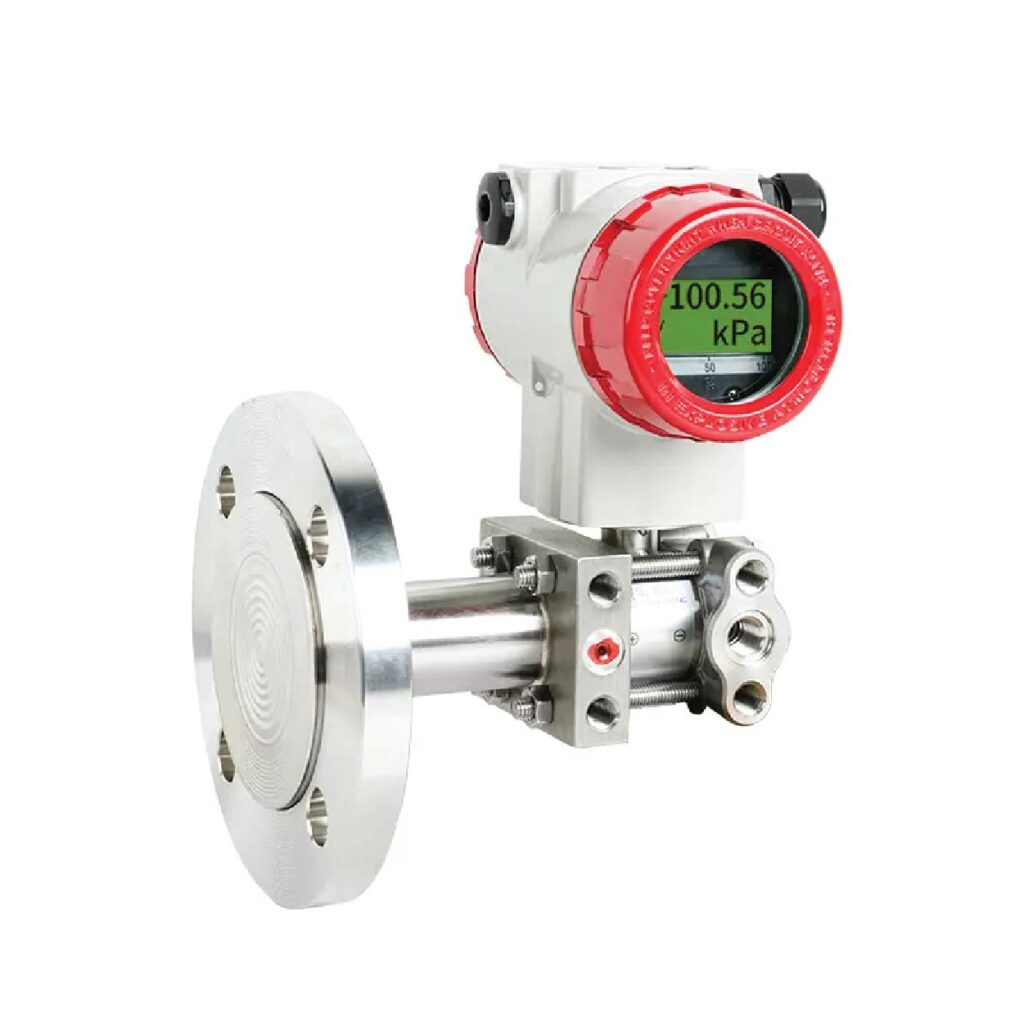

vel transmitters measure the level of liquids in tanks and vessels.
Applications:
Measuring crude oil levels in storage tanks.
Monitoring water or chemical levels in injection processes.
Preventing overflows or excessively low levels of liquids.
Features:
High accuracy, even in environments with steam or various gases.
Available types include radar and ultrasonic level transmitters.
5. Control Valves
Control valves play a crucial role in regulating fluid flow and controlling pressure, temperature, and levels.
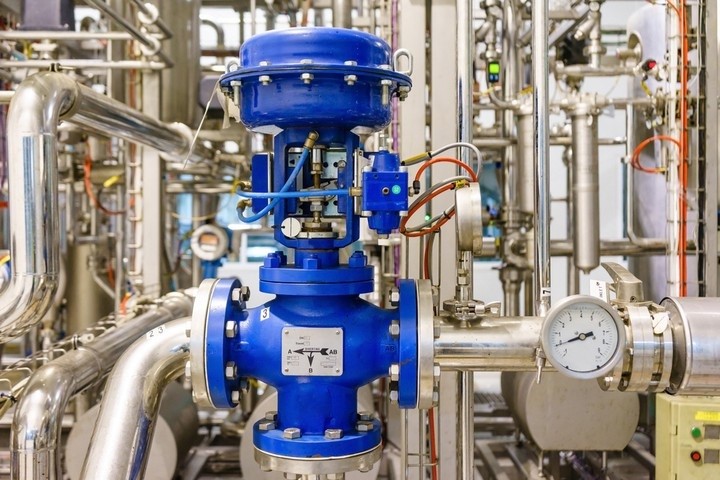

Applications:
Regulating gas pressure in transmission lines.
Controlling oil flow in refining processes.
Preventing fluctuations in sensitive processes.
Features:
High response speed.
Resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
6. Gas Analyzers
These systems measure and analyze the composition of gases in various processes.
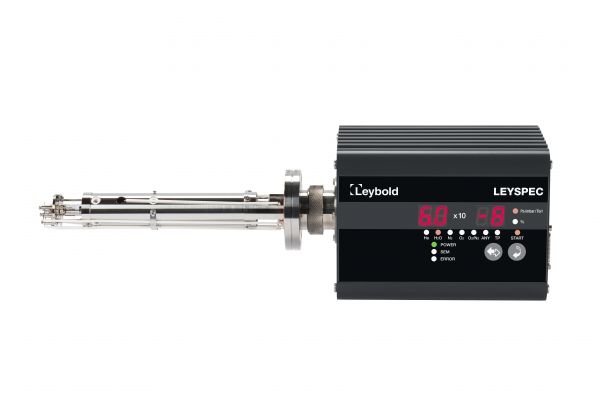

Applications:
Analyzing gas compositions from oil and gas wells.
Monitoring emissions to comply with environmental standards.
Controlling combustion processes in turbines and boilers.
Features:
High accuracy in analyzing various gases.
Capability to operate in hazardous environments.
7. Safety Systems

Safety systems include various instruments designed to detect and mitigate potential hazards.
Applications:
Detecting leaks of gas or flammable vapors.
Triggering alarms for abnormal pressure, temperature, or levels.
Emergency shutdown of processes in dangerous conditions.
Common Systems:
Gas detectors.
Pressure and temperature cutoff switches.
8. Data Loggers
Data loggers collect and store data related to various process parameters.
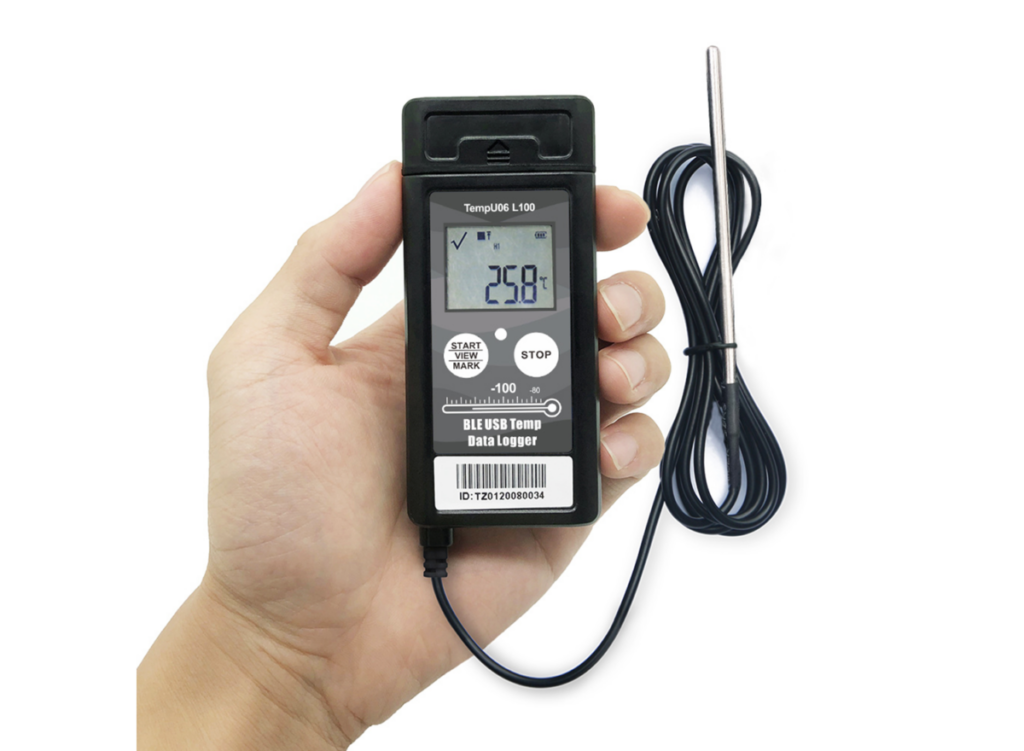

Applications:
Recording pressure, temperature, and flow data for future analysis.
Assisting in process optimization.
Generating detailed reports for management and inspections.
Features:
High storage capacity.
Compatibility with SCADA systems.
9. Distributed Control Systems (DCS) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
These systems manage and monitor entire processes.

Applications:
Automated control of refining and transmission operations.
Monitoring all instrumentation equipment.
Real-time data analysis and decision-making.
Features:
High flexibility.
Integration with other equipment.
10. Sensors
Sensors are fundamental components of many instrumentation devices, providing critical information for process control.
Applications:
Detecting changes in temperature, pressure, and flow.
Sending data to control systems.
Ensuring operational safety and stability.
Features:
High accuracy.
Long lifespan in challenging environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Instrumentation plays a pivotal role in monitoring, controlling, and ensuring the safety of processes in the oil and gas industry. Equipment such as pressure and temperature transmitters, flow meters, control valves, and safety systems are among the most commonly used tools in this sector. Proper selection and efficient utilization of these tools significantly enhance productivity and safety while reducing costs.

